Hemorrhoids Treatment of Symptoms
Hemorrhoids are enlarged and swollen veins around the outside of the anus or at the bottom of the rectum. The rectum is the last part of the intestine and leads to the anus, the opening at the end of the intestine through which feces are removed from the body. All people have hemorrhoidal tissue in this area that is made up of blood vessels and veins, connective tissue and some muscle. This tissue does not enlarge or swell in all cases, but over time, this phenomenon is more likely to occur, causing a condition known as hemorrhoidal disease. Hemorrhoids require treatment for the relief of the symptoms they cause.
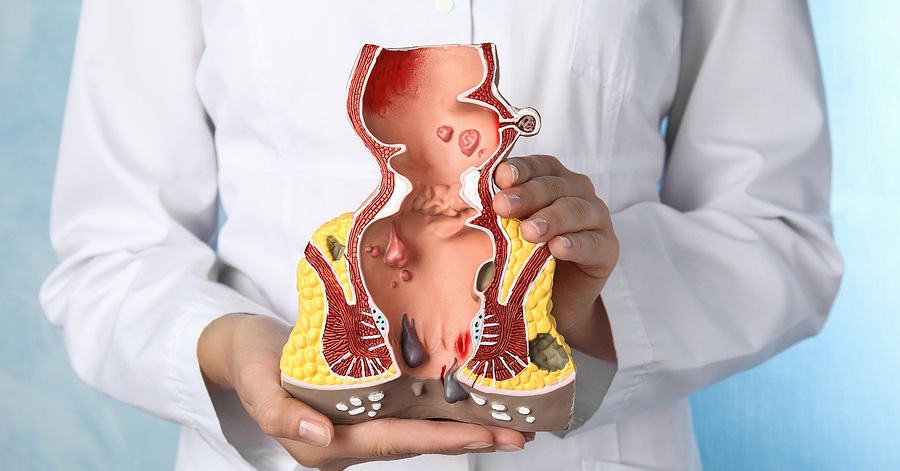
Hemorrhoids Classification
Hemorrhoids are either internal or external. Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum and are usually not visible to the naked eye. Internal hemorrhoids generally do not cause pain, but often present painless bleeding from the rectum. In some cases, internal hemorrhoids can protrude through the anus and be visible, a phenomenon called prolapse. When this happens, they will usually shrink back into the rectum on their own or can be pushed back.
Internal hemorrhoids, depending on the degree of prolapse, can be classified into further categories. In internal hemorrhoids of the 1st degree, no prolapse is found, only the blood vessels protrude. In the 2nd degree, prolapse occurs during bowel movement, but there is immediate automatic recovery. In grade 3 internal hemorrhoids, the prolapse is visible but the hemorrhoids can be manually pushed back into place, while in grade 4 prolapse the prolapse cannot be manually retracted.
External hemorrhoids develop under the skin around the outside of the anus. These are associated with increased rates of patient discomfort, as they often itch or are painful. In some cases, a blood clot may form in an external hemorrhoid, creating a clotted hemorrhoid, which can lead to severe, continuous pain.
Hemorrhoids Causes
Many conditions and habits are believed to cause hemorrhoids. The main ones include chronic constipation or diarrhea, intense straining during bowel movements and staying on the toilet for a long time. Stress, constipation, and prolonged sitting can all affect blood flow to the area, causing blood to not move at the expected rate through the vessels, causing hemorrhoids to appear.
Factors that increase the risk of hemorrhoids include a lack of dietary fiber and obesity. The risk factors for the manifestation of the condition include advanced age, while it is very likely that hemorrhoids will occur during pregnancy. The problem usually goes away after the fetus is born.
Hemorrhoids Symptoms
Bleeding during bowel movements is one of the main symptoms of hemorrhoids. Other symptoms include the appearance of bright red blood on the toilet paper or in the stool after a bowel movement, itching and a burning sensation in the anal area. A frequent symptom is also pain both in the anal area, especially when the patient is sitting, and during bowel movements. At the same time, one or more hard, painful lumps may be found around the anus. The rarest symptoms of hemorrhoids, especially if the rectal mucosa is prolapsed, are unpleasant odor and gas or stool incontinence.
Hemorrhoids Diagnosis
In order to diagnose hemorrhoids, a detailed patient history is taken, followed by a clinical examination of the rectum and anus. In some cases, an X-ray examination using an opaque enema is indicated, while an endoscopic examination may also be recommended. Endoscopic methods used to diagnose the condition include sigmoidoscopy, anoscopy, and colonoscopy. It is important to carry out a thorough examination to exclude the existence of diseases that manifest with similar symptoms, such as fissure, abscess or fistula of the anus, or colon cancer.
Hemorrhoids Treatment
The treatment of hemorrhoids depends on the stage of the condition and the severity of the symptoms. The treatment of 1st and 2nd degree hemorrhoids is usually conservative, with dietary changes and administration of ointments and suppositories. As for changes in eating habits, the consumption of fiber and plenty of water is recommended in order to treat constipation. A high-fibre diet can make stools softer to deal with straining, while spicy or fatty foods and alcohol consumption is important to be avoided. At the same time, it is advisable to maintain proper hygiene of the anus, to reduce the time spent sitting on the toilet, while after the end of every bowel movement it is recommended to wash with water and not to use tissue paper.
There are a number of non-surgical treatments for hemorrhoids, including infrared or laser photocoagulation, rubber ligation, cryosurgery, sclerotherapy, and the use of staples, which cut away excess tissue to cause hemorrhoids. Grade 3 and 4 hemorrhoids are treated surgically. The most common procedure is a hemorrhoidectomy, in which the hemorrhoids are removed and the wound is either sutured or left to heal on its own. The most modern and bloodless technique is hemorrhoids laser treatment, which cauterizes the hemorrhoidal tissue using local anesthesia.

